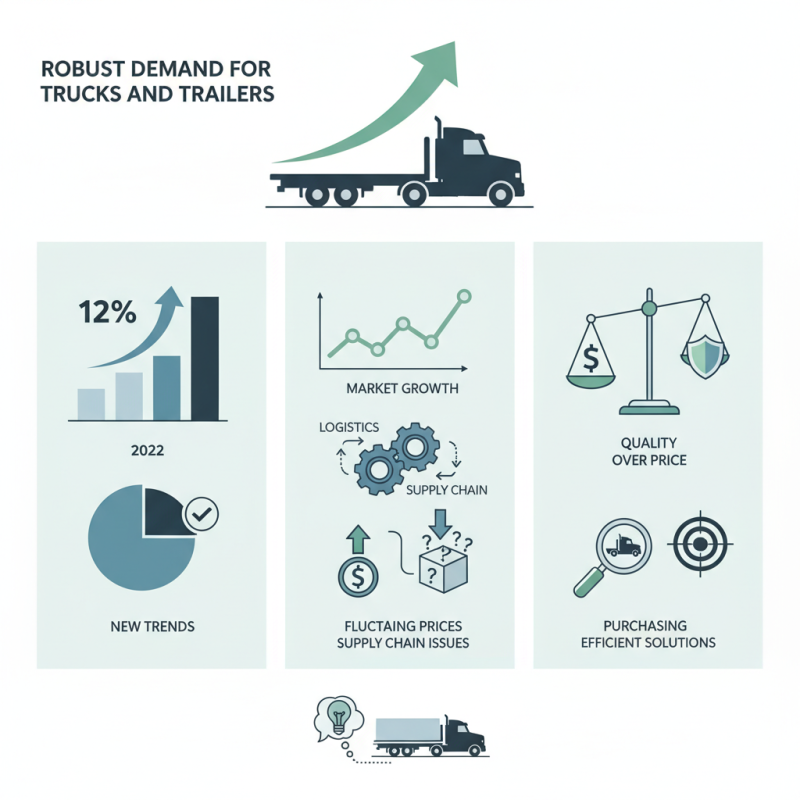
The demand for trucks and trailers remains robust, especially in the logistics and transportation sectors. As of late 2023, the industry reports show a significant increase in "truck and trailer for sale" listings, highlighting the ongoing growth in this market. According to a recent data analysis from transportation expert John Anderson, “The market is evolving, and we must adapt to new trends.” His insights resonate well as businesses seek more efficient delivery solutions.
Recent statistics indicate a 12% increase in sales of trucks and trailers compared to the previous year. This growth may point to an expanding economy, but it also brings challenges. Suppliers may struggle with fluctuating prices and supply chain issues. The availability of "truck and trailer for sale" options is critical for buyers navigating this dynamic landscape.
It is essential to continuously reassess purchasing strategies in this competitive environment. Focusing solely on price may lead to missed opportunities for long-term reliability. As John Anderson cautions, “Quality still matters.” It's a reminder to balance cost with value in the quest for optimal transportation solutions.
The Importance of Renewable Energy in Modern Society
Renewable energy is crucial in today's society. It plays a key role in combating climate change. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewables accounted for 29% of global electricity generation in 2020. This number continues to rise, signaling a shift in energy consumption patterns.
Solar and wind energy are at the forefront of this transition. The Global Wind Energy Council reported a 53% increase in global wind power capacity in 2020. Despite these advancements, challenges remain. Infrastructure investment is often lacking. This creates limitations in energy distribution, especially in remote areas.
Moreover, while renewable sources are cleaner, some implementations have drawbacks. The production of solar panels can release harmful chemicals. This raises questions about sustainability in their lifecycle. Finding a balance between renewable energy growth and environmental safety is essential. We need to progress cautiously and thoughtfully.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources and Their Benefits
Renewable energy sources are crucial for a sustainable future. They offer diverse benefits, from reducing greenhouse gas emissions to promoting energy security. Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy are examples of renewable sources. According to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), renewable energy could power up to 86% of the world by 2050.
Solar energy harnesses sunlight to generate electricity. It's available anywhere on Earth and can reduce utility bills. Wind energy, primarily captured through turbines, is another efficient source. Many countries now generate significant power from wind, showcasing its potential. In 2021, wind energy alone accounted for 15% of global electricity production.
Tip: Look into local incentives for renewable energy installations. They can help offset initial costs while maximizing savings.
Hydropower utilizes flowing water to generate electricity. It remains the largest source of renewable energy globally. However, its impact on local ecosystems must be considered. Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s heat, providing stable energy across various regions. This energy source is less recognized but holds substantial promise.
Tip: Evaluate your region's renewable options. Some areas may benefit more from solar than wind or vice versa.
Choosing renewable energy contributes to cleaner air and combats climate change. Yet, we must critically assess environmental impacts. Are we truly utilizing these resources sustainably? Balancing energy needs and ecological health is a challenge that requires ongoing reflection.
The Economic Impact of Transitioning to Renewable Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy has significant economic implications. According to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the renewable energy sector could create up to 24 million jobs by 2030. This shift not only supports employment but also stimulates local economies.
Investments in renewable energy drive innovation. The International Energy Agency (IEA) states that investments in renewables led to over $300 billion in new projects in 2020. Clean energy technologies enhance energy efficiency and decrease dependence on fossil fuels. However, transitioning industries may face challenges, including job losses in traditional sectors. Balancing these shifts requires careful planning and retraining programs.
**Tip:** Consider your community's potential for renewable energy projects. Renewable energy can lower local energy costs in the long run.
Investing in complexity is essential. Some regions excel in solar, while others are suited for wind. This regional disparity may cause uneven growth, provoking economic divides. Therefore, tailored approaches to energy transition are necessary. Planners must analyze local resources and workforce capabilities for a successful transition to renewable energy.
The Economic Impact of Transitioning to Renewable Energy
This chart illustrates the economic benefits associated with transitioning to renewable energy. The data highlights the potential for job creation, investment growth, reduction in energy costs, increased energy independence, and significant environmental benefits, all expressed in billions of dollars.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Renewable Energy Solutions
Implementing renewable energy solutions presents numerous challenges. One major issue is the variable nature of sources like solar and wind. Energy production can fluctuate based on weather conditions. Grid stability becomes a concern with these inconsistencies. An unexpected storm can significantly reduce output. Therefore, energy storage solutions are essential but often costly and complex.
Additionally, public acceptance plays a crucial role. Communities may resist new installations due to aesthetic concerns or a lack of understanding. Education efforts are vital but can be slow. Misconceptions about renewable energy hinder progress. Moreover, existing infrastructure often requires upgrades to accommodate new technologies. This adds to the financial burden for governments and companies alike.
Despite these hurdles, innovative solutions are emerging. Microgrids offer localized energy management. They can enhance resilience in communities. However, not all areas have access to such advancements. Policymakers must address disparities. Collaboration between stakeholders is key to overcoming these hurdles and fostering a sustainable future.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Renewable Energy Solutions
| Challenge | Description | Solution | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Initial Costs | Many renewable energy technologies require substantial upfront investment. | Implementing financing options and incentives can lower initial costs. | Increased accessibility to renewable energy technologies. |
| Intermittency | Renewable sources like solar and wind are not always available. | Energy storage systems and grid integration can help manage supply. | Improved reliability and stability of energy supply. |
| Regulatory Barriers | Complex regulations can hinder the deployment of renewable technology. | Streamlining permitting processes can facilitate faster implementation. | Accelerated project development and operation timelines. |
| Public Perception | Misunderstanding and skepticism about renewable energy technology. | Educational campaigns and outreach can inform the public. | Higher acceptance and support for renewable initiatives. |
| Technology Maturity | Some renewable technologies are still developing and lack efficiency. | Investing in R&D can accelerate technological advancements. | Greater efficiency and lower costs over time. |
Future Trends in Renewable Energy Technologies and Innovations
The future of renewable energy technologies is exciting yet complex. As we innovate, we face challenges. For instance, batteries are crucial for energy storage. But current battery technology still struggles with efficiency and recycling. Many designs are too bulky or expensive, limiting their use in everyday applications.
Wind and solar power continue to evolve. However, energy production can be inconsistent. Weather conditions impact efficiency. Researchers are working on smart grid technologies. These systems optimize energy distribution and enhance reliability. Yet, the integration of these systems remains a work in progress.
Hydrogen fuel cells show promise too. They offer clean energy, but production is often energy-intensive. We must consider the source of hydrogen. Sustainable hydrogen is still a goal rather than a reality. Overall, while innovations abound, the renewable energy sector still requires significant reflection and improvement.
